In addition to a much larger variety of corals, reefs of Lau seem to have an unusually large number of fluorescent, brightly colored corals, more than we’ve seen in past expeditions. Corals are usually light or golden brown, but some may be bright blue, green or even red and they can fluoresce, mainly through specialized cells and pigments. They can change color, depending on the environmental conditions they encounter, and they can also become white or translucent when stressed. Hence, for colorful corals, color is an important indicator of the health of the coral.
What Makes Colorful Corals Colorful?
The colors found in colorful corals are mostly due to three things – photosynthetic pigments, fluorescent proteins and non-fluorescent chromoproteins.
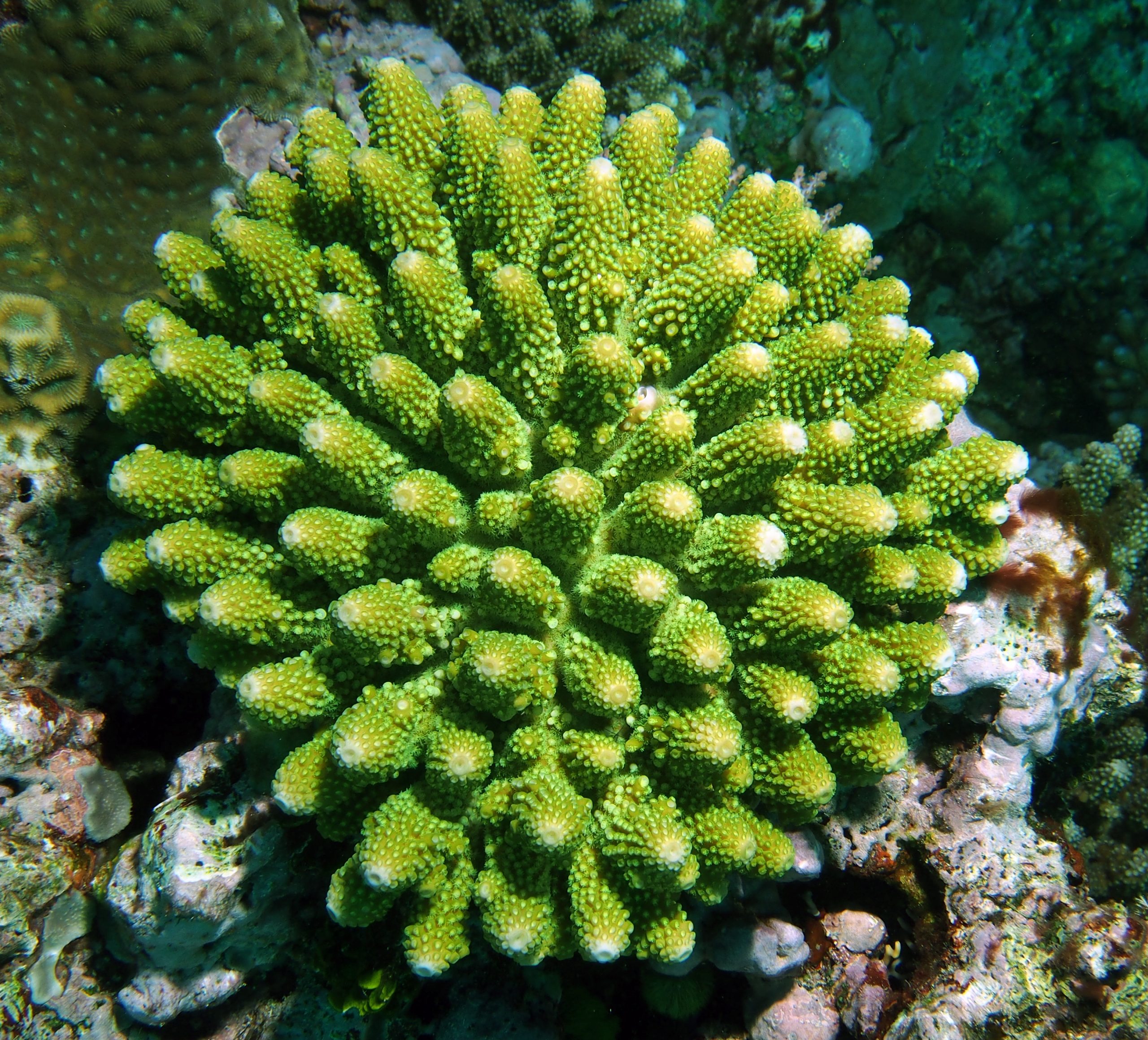
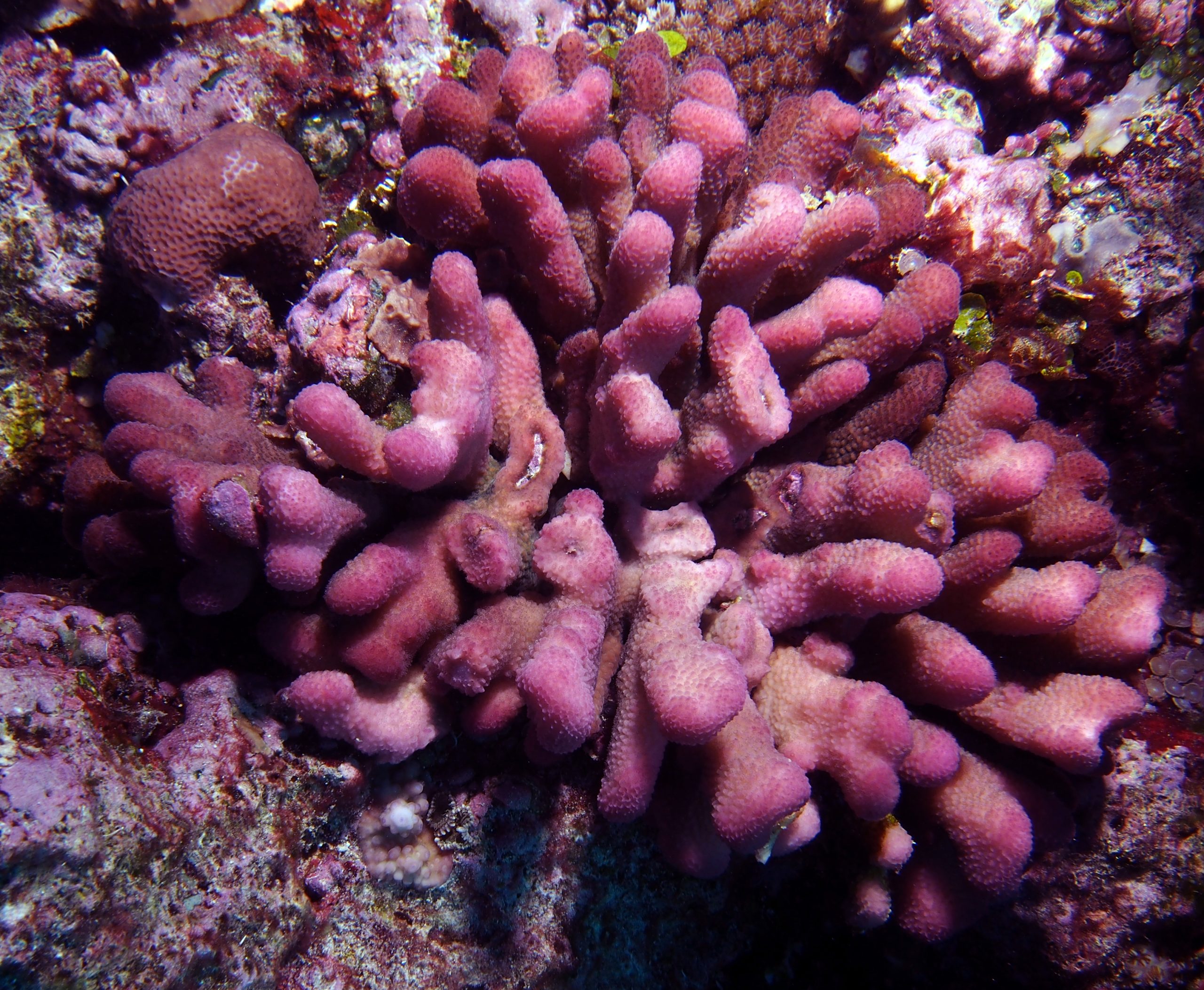


Colorful corals contain symbiotic algae, or zooxanthellae, which are brownish or green because of the photosynthetic pigment called “chlorophyll”. The chlorophyll is responsible for the brown or green coloration. The zooxanthellae are light sensitive, increasing or decreasing based on available light intensities, and as a result becoming darker or lighter. Chlorophyll can also fluoresce a deep red color under special circumstances. Corals host several types of zooxanthellae, often referred to as “Clades” which have different tolerances for temperature and light; under stressful conditions the coral may expel the zooxanthellae, becoming white or “bleached”.
Phycoerythrin, another photosynthetic pigment found in zooxanthellae, fluoresces a bright orange color. This is visible in the day, especially in a branching coral called Pavona maldivensis.
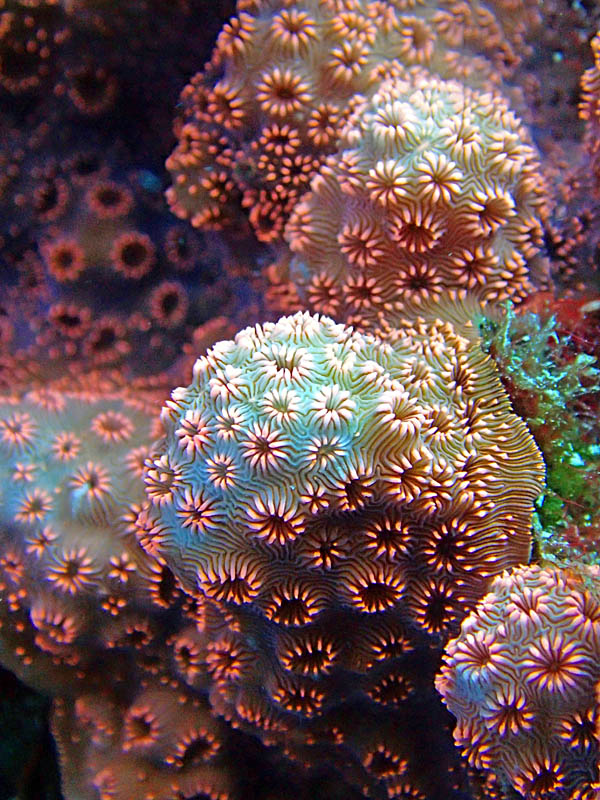


There are also pigments produced by the coral animal that are non-fluorescent ‘reflective’ proteins referred to as “chromoproteins”. These pigments can appear red, purple, blue, mauve or other colors. There are about two dozen chromoproteins found in colorful corals.
There are also more than 85 fluorescent pigments that are produced by colorful corals. These proteins absorb light of one color (wavelength) and emit (fluoresce) a different (lower energy wavelength) color. These pigments are usually cyan, green, yellow or red, and will glow when viewed with certain types of lights.
Colorful Corals, Coral Health, and Resilience
The pigments are thought to play a major role in the health and resilience of the corals, and how well the corals are able to interact with their environment. For instance, pigments may help protect the coral from damaging sunlight, or other forms of stress. A recent study found a dramatic decline in fluorescence due to unusually cold or warm waters. If the corals acclimated to cold stress, fluorescence returns to normal. Under heat stress conditions, there is initially a spike in fluorescence, then a decline as the corals bleach. Chromoproteins take up substantial amounts of light, but they don’t re-emit the light. The screening effect may help the corals take up new symbionts after bleaching.

To follow along and see more photos, please visit us on Facebook!